An SUV with attitude was the inspiration behind the design of the all-new 2019 Chevrolet Blazer. (Fig. 1) The midsize Blazer slots between the Equinox and Traverse in the Chevy lineup and has seating for five along with up to 64.2 cubic feet of cargo space.
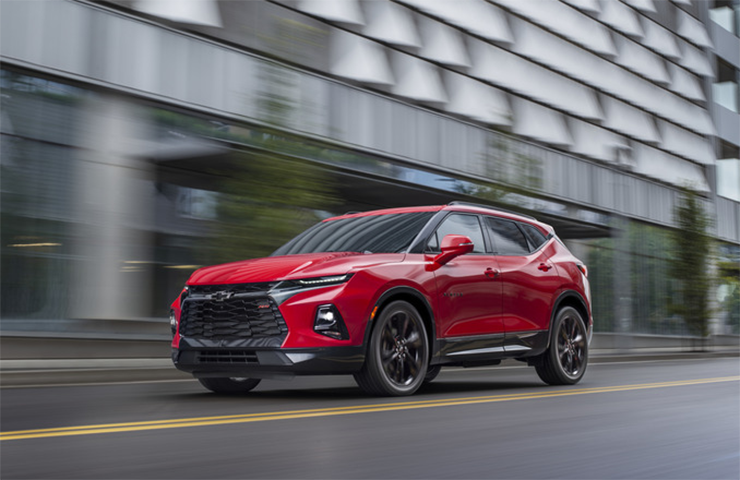 Fig. 1
Fig. 1
Available in four trim levels: entry-level L (Blazer 2.5 in Canada), mid-level Blazer, sport-inspired RS, and top-of-the-line Premier, each model in the lineup features unique grille appearances and a distinctive lighting execution with low-placed HID headlamps. (Fig. 2)
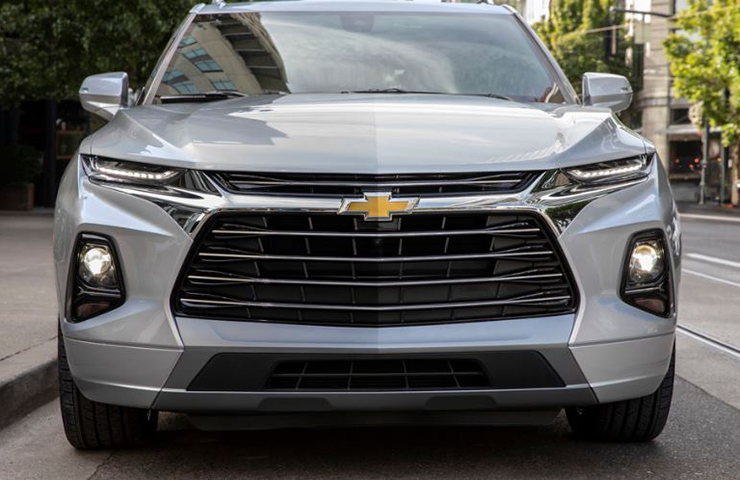 Fig. 2
Fig. 2
Powertrain
The Blazer is available with a 2.5L 4-cylinder engine (RPO LCV) that is paired with the 9T50 9-speed automatic transmission (RPO M3D) or a 3.6L V6 engine (RPO LGX) mated to the 9T65 9-speed automatic transmission (RPO M3V). The advanced twin-clutch all-wheel-drive system is optional.
The standard 2.5L 4-cylinder engine (Fig. 3) is rated at 193 hp and 188 lb-ft of torque. The optional 3.6L V6 generates 305 hp and 269 lb-ft of torque. Both direct-injected engines feature an intelligent stop/start system to improve fuel efficiency.
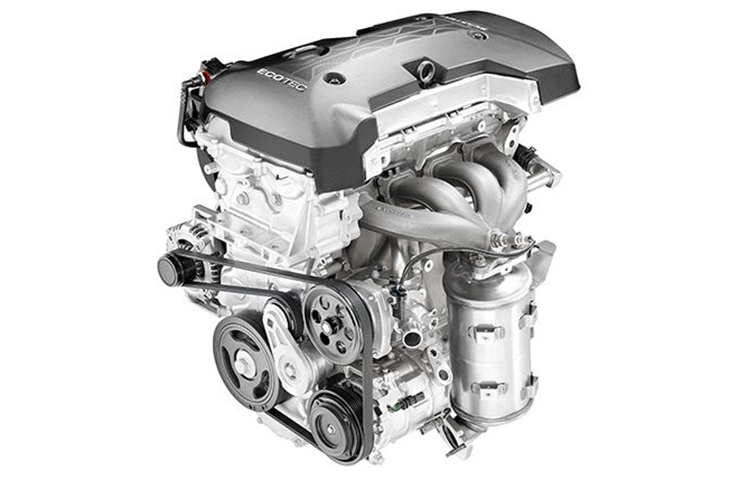 Fig. 3
Fig. 3
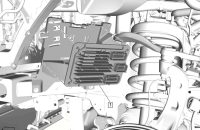
The 3.6L V6 engine (Fig. 4) features Active Fuel Management (AFM) to increase fuel efficiency. With the AFM system on, the Oil Control Valve (OCV) directs oil to the dual-feed hydraulic lash adjuster, which unlatches the switching roller finger followers, creating zero lift and not allowing the valves to open on cylinders two and five. With the AFM system off, the OCV is not active and oil is not directed to the dual-feed hydraulic lash adjuster.
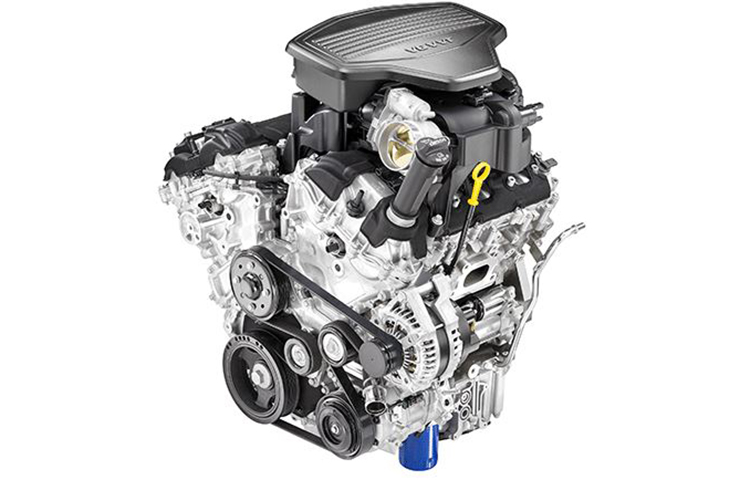 Fig. 4
Fig. 4
The 2.5L 4-cylinder engine uses dexos1 GEN 2 full synthetic SAE 0W-20 viscosity grade engine oil. The 3.6L V6 engine uses dexos1 GEN 2 full synthetic SAE 5W-30 viscosity grade engine oil.
Both engines have an air filter life system where the Driver Information Center displays an estimate of the engine air filter’s remaining useful life and the state of the system.
The Hydra-matic 9T50 and 9T65 are fully automatic, 9-speed, transverse-mounted, electronic-controlled transmissions. They consist primarily of a 4-element torque converter, a compound planetary gear set, friction and mechanical clutch assemblies, and a hydraulic pressurization and control system. Both transmissions use DEXRON-VI Automatic Transmission Fluid.
AWD Systems
Traction Select is standard on all models and allows the driver to make real-time adjustments to the vehicle’s driving mode to account for varying road conditions. On AWD models, it also allows the system to be completely disconnected from the rear axle so the vehicle can operate in FWD when AWD capability is not needed.
The more sophisticated twin-clutch AWD system that is available on RS and Premier models helps optimize traction by preemptively and electronically splitting the torque as needed between the rear wheels using twin clutches. With the twin-clutch design, it is capable of transferring up to 100 percent of available torque to the front or rear axles. Also, across the rear axle, the electronically-controlled rear differential can direct up to 100 percent of available torque to either wheel.
Chassis Features
To improve the steering feel of the Blazer and reduce common vibrations from rough roads or the powertrain at idle, a tuned vibration absorber is integrated into the steering wheel.
The Blazer is equipped with a TRW EBC460 brake system. The K17 electronic brake control module (EBCM) and the brake pressure modulator are serviced separately. The system features Dynamic Rear Proportioning, Intelligent Brake Assist, StabiliTrak Electronic Stability Control, Traction Control, and available Trailer Sway Control.
The Blazer offers a range of wheels, including standard 18-inch wheels, available 20-inch wheels, and 21-inch wheels on the RS and Premier models. On RS and Premier models equipped with 21-inch wheels and tires (Fig. 5), the suspension also features an auxiliary spring aid that’s internal to each of the springs and a load management striker cap (LMSC) on the rear dampers to help give the vehicle better ride performance. The LMSC absorbs some of the energy when a vehicle is driven on rough roads. The auxiliary spring aid absorbs energy as well and provides another load path to the chassis.
 Fig. 5
Fig. 5
Driver Assistance Systems
A number of driver assistance and safety technologies are available on the Blazer (Fig. 6) to help the driver better monitor the vehicle’s surroundings and respond in the event of an unexpected circumstance. The systems use a combination of camera, short and long range radars, and ultrasonic sensors. When fully equipped with all of the available safety features, there are a total of three radars, six cameras and eight ultrasonic sensors. Available systems include Adaptive Cruise Control, a digital Rear Vision Camera, Following Distance Indicator, Forward Automatic Braking, Front Pedestrian Braking, Lane Keep Assist with Lane Departure Warning, a Rear Camera Mirror, and a Safety Alert Seat.
 Fig. 6
Fig. 6
The Blazer also has seven airbags and an innovative 360-degree sensor system designed to measure the severity of a crash and adjust airbag inflation accordingly for proper deployment.
Infotainment
The Chevrolet Infotainment 3 system (RPO IOR) with an 8-inch diagonal color touchscreen is standard on the Blazer. The Chevrolet Infotainment 3 system with navigation and an 8-inch diagonal color HD touchscreen (RPO IOT, IOU) as well as the uplevel Bose Premium eight speaker system (RPO UQA) are available on several trim models. (Fig. 7)
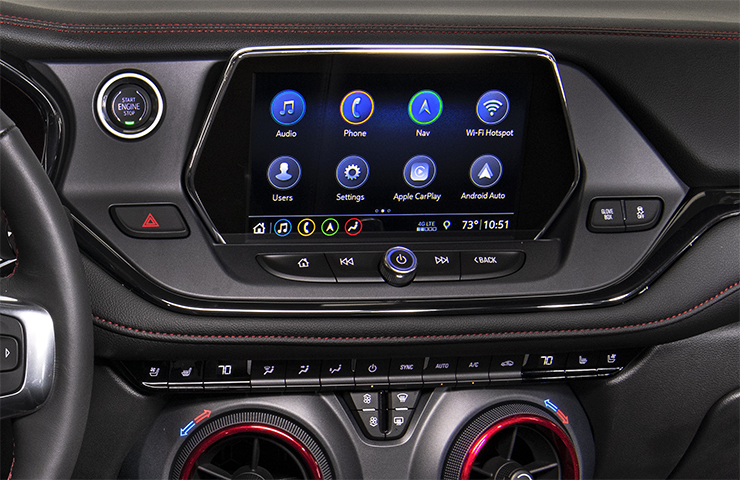 Fig. 7
Fig. 7
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) technology, which uses four microphones in the cabin to monitor for unwanted low-frequency engine-produced noises and projects indistinguishable sound waves to counteract the unwanted noise, is standard on all models.
Vehicle Lifting
When lifting the vehicle with a frame-contact lift, place the front lift pads on the front lower brackets, inboard of the rocker pinch weld flange and outboard of the front frame rail, at the torque box location. Place the rear lift pads on the rear frame rail, at the torque box location. (Fig. 8)
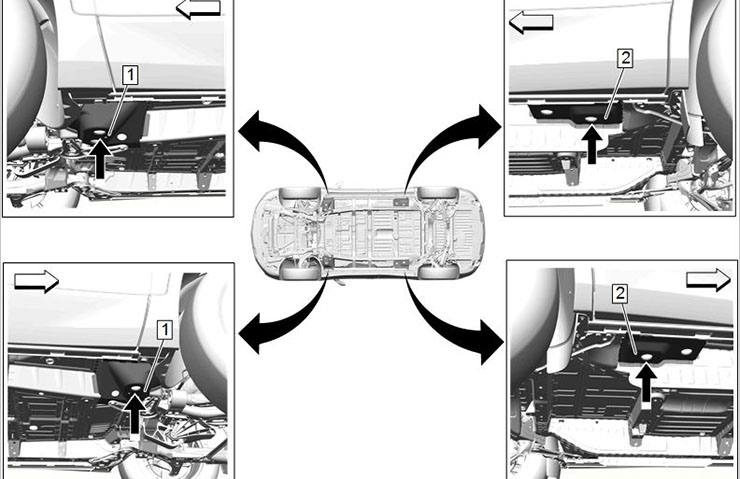 Fig. 8
Fig. 8
When transporting a disabled vehicle use the specific front attachment points to pull the vehicle onto the flatbed car carrier. (Fig. 9)
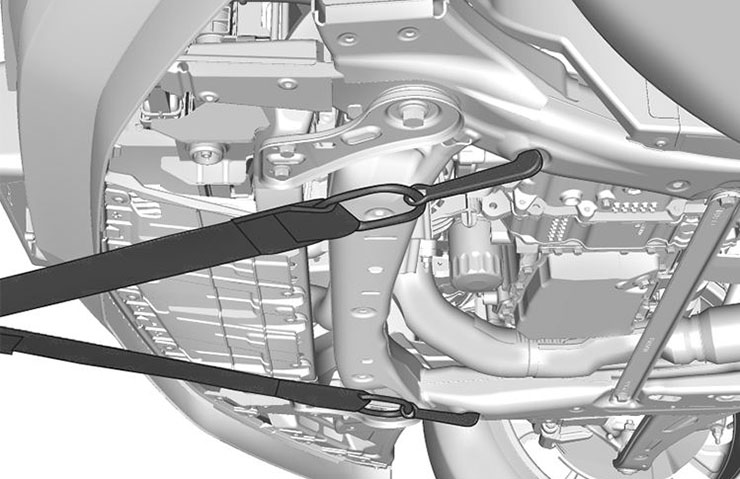 Fig. 9
Fig. 9
For more information on the new 2019 Blazer, check out the web-based training course 10319.11W: Chevrolet Blazer New Model Launch and refer to Bulletin #18-NA-373.
– Thanks to Kris Villegas and Sherman Dixon