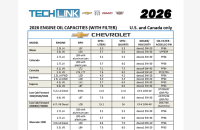
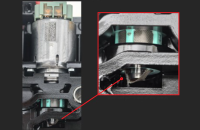
GM’s Global Architecture, or Global A, electrical system does not allow control modules to be swapped between vehicles. (Fig. 10) This has been true since the first Global A vehicles were introduced in 2010; however, the Techline Customer Support Center (TCSC) continues to get calls asking for assistance after control modules have been switched on two vehicles.
 Fig. 10
Fig. 10
Swapping control modules, including the ECM, BCM, EBCM, SDM, TCM, ECC (HVAC), EPS, HPCM, IPC, and Radio, between vehicles will damage both controllers and will result in a no start condition on both vehicles due to the new vehicle security code protocol.
These modules all have IDs that must match in order for the BCM to allow starting the engine. The control modules are coded to the vehicle when they are first programmed, which results in a unique ID being permanently stored in that module. Swapping these security-related modules will cause difficult and time-consuming remediation processes that may include the purchase of new components for both vehicles.
Global A models include:
2010-2018 SRX
2010-2019 LaCrosse, Camaro, Equinox, Terrain
2011-2019 Regal, Cruze
2012-2018 Verano
2012-2019 Sonic, Volt
2013-2019 Encore, ATS, XTS, Spark, Trax
2014 Silverado 1500, Sierra 1500
2014-2018 ELR, Caprice PPV, Spark BEV, SS
2014-2019 CTS, Corvette, Impala
2015-2019 Escalade, Colorado, Silverado, Tahoe, Suburban, Canyon, Sierra, Yukon
2017-2019 XT5, Acadia
2018-2019 Enclave, Traverse
2019 XT4, Silverado 1500, Sierra 1500
GM’s diagnostic strategy does not support the practice of swapping control modules during the course of diagnosis or in order to expedite a repair. Features in today’s vehicles are increasingly software-configurable. They can affect vehicle safety systems, anti-theft systems, performance, and customer personalization information.
Security Methods
There are a number of security methods in operation in the vehicles built using the Global A electrical architecture.
Security Code – The purpose of the security code is to protect the vehicle’s security information against tampering. It’s a random code, unique to each vehicle, generated at the vehicle assembly plant. The assembly plant stores the security code and the corresponding VIN for each vehicle. A correct security code match is required to allow specific vehicle theft deterrent functions to be performed. An example of this function is the learning of new key fobs to the vehicle.
Environmental ID – The purpose of the Environmental ID is to increase the time and complexity involved in attempting a vehicle theft by swapping control modules. The Vehicle Theft Deterrent Feature provides the capability to detect if modules have been substituted, indicating a potential theft situation, and will not allow continued running of the engine in that case.
Seed and Key – The purpose of Seed and Key is to protect certain control modules from unauthorized reprogramming when they are outside of the assembly plant environment. Each control module that implements Seed and Key is manufactured with a unique seed value and a corresponding key value stored in memory. The seed is a value that is reported to a reprogramming tool. The reprogramming tool must know the matching key value to unlock the control module so that it can be programmed. The reprogramming tool then sends the matching key to the control module. There is no way to read the key value out of a control module.
Symptoms of Module Swapping
A variety of symptoms may appear in a Global A vehicle containing one or more control modules swapped from a like vehicle. Depending upon which control modules have been swapped, possible symptoms include:
- The VIN read by GDS and SPS does not match the vehicle.
- Current DTC B3902 – Incorrect IMMO ID Rec. set in IPC, SDM, ECM, HVAC, Steering Column Lock Control Module (if equipped) or BCM. There are no warning lamps or DIC messages and this DTC cannot be cleared.
- IPC module displays (- – -) for odometer and trip odometer values.
- Vehicle will enter power mode only if the key fobs that match the donor vehicle BCM are included in the swap.
- BCM and/or ECM has current DTC B389A – Environment Identification. There is a Service Theft System message on the DIC, the Security MIL is illuminated and this DTC cannot be cleared.
- ECM odometer value is incorrect for vehicle.
- Radio displays Locked
On today’s new models, it’s incredibly difficult to keep track of which control modules cannot be swapped. Electrical architecture, model, model year, sales region, vehicle option content and configuration all play a role in how a vehicle is equipped and if swapping a module will be an issue. The best way to avoid it is to simply not do it.
– Thanks to Bret Raupp
























Great information