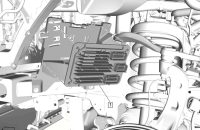
Several high-pressure exhaust charge DTCs may set on some 2019-2022 Silverado, Sierra; 2021-2022 Tahoe, Suburban, Escalade; and 2022 Yukon models equipped with the 5.3L engine (RPO L84) or 6.2L engine (RPO L87). (Fig. 1) The Check Engine MIL also may be illuminated.
DTCs that may set include:
- DTC P3189 – Cylinder 1 Trapped High Pressure Exhaust Charge
- DTC P318A – Cylinder 2 Trapped High Pressure Exhaust Charge
- DTC P318B – Cylinder 3 Trapped High Pressure Exhaust Charge
- DTC P318C – Cylinder 4 Trapped High Pressure Exhaust Charge
- DTC P318D – Cylinder 5 Trapped High Pressure Exhaust Charge
- DTC P318E – Cylinder 6 Trapped High Pressure Exhaust Charge
- DTC P318F – Cylinder 7 Trapped High Pressure Exhaust Charge
- DTC P3190 – Cylinder 8 Trapped High Pressure Exhaust Charge
 Fig. 1
Fig. 1
These conditions may be related to a prior engine replacement or major engine repair in which the crankshaft position variation learn procedure was not completed.
The crankshaft position sensor variation or reluctor ring learn is used to calculate reference period errors caused by slight tolerance variations in the crankshaft and the crankshaft position sensor. The calculated error allows the ECM to accurately compensate for reference period variations, which enhances the ability of the ECM to detect misfire events over a wider range of engine speed and load. The compensation values are stored in ECM memory after a learn procedure has been performed.
If any of the exhaust charge DTCs are set, the crankshaft position variation learn should be performed. Once the procedure is completed, verify the DTCs have not returned. If the codes are still present, follow the diagnostics in the appropriate Service Information.
DTC Diagnostic
In the Dynamic Fuel Management (DFM) cylinder deactivation system, the intake and exhaust lifters are disabled consecutively so that a low-pressure charge is trapped in the cylinder. The DFM lifters are deactivated after the exhaust valve opens and before the intake valve opens.
The exhaust charge DTC diagnostic looks at crank speed to determine whether there was a deactivation error (either in timing or in hardware) prior to the exhaust stroke. If deactivation occurs between the intake valve opening and the exhaust valve opening, air could be drawn in during the intake portion, compressed and burned, but never exhausted, leaving a high-pressure charge trapped in the cylinder that will get compressed on the next engine cycle TDC and spring back afterwards. The diagnostic tries to detect this spring effect by measuring the crank speed variation.
It also may be difficult to isolate the correct cylinder when these DTCs are set. The concern may be caused by a cylinder on the opposite bank from the location of the DTC. Be sure to inspect the other side of the engine bank for any valvetrain concerns associated with these DTCs.
– Thanks to Tim Lightfoot